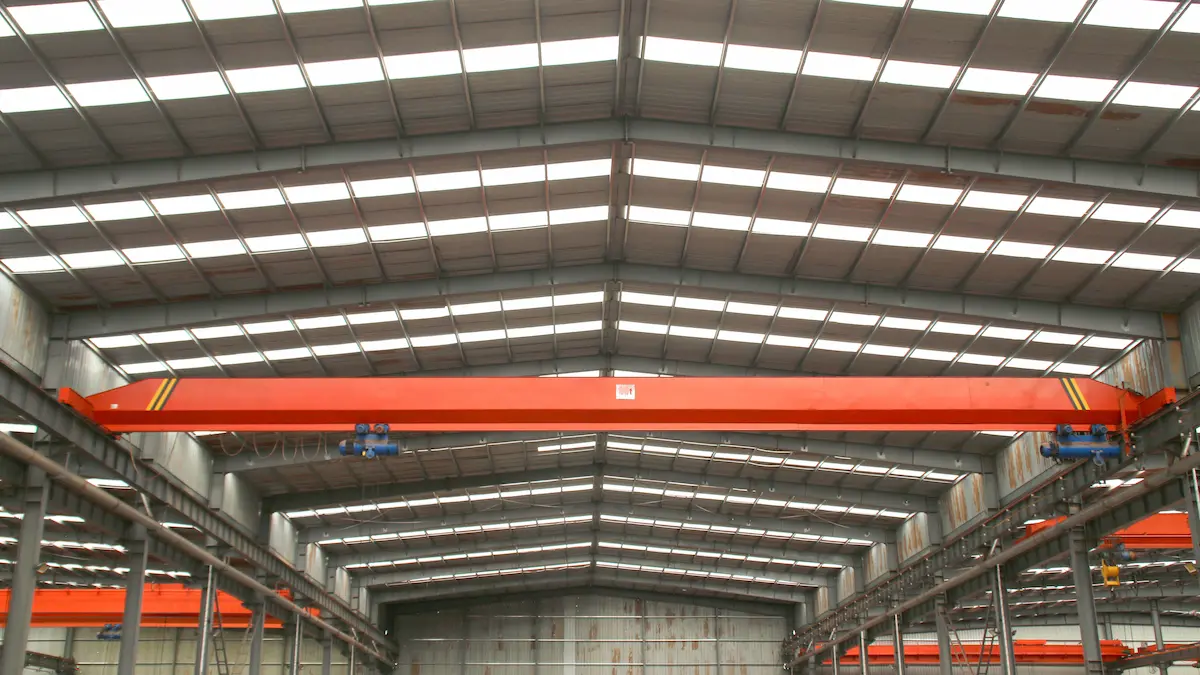
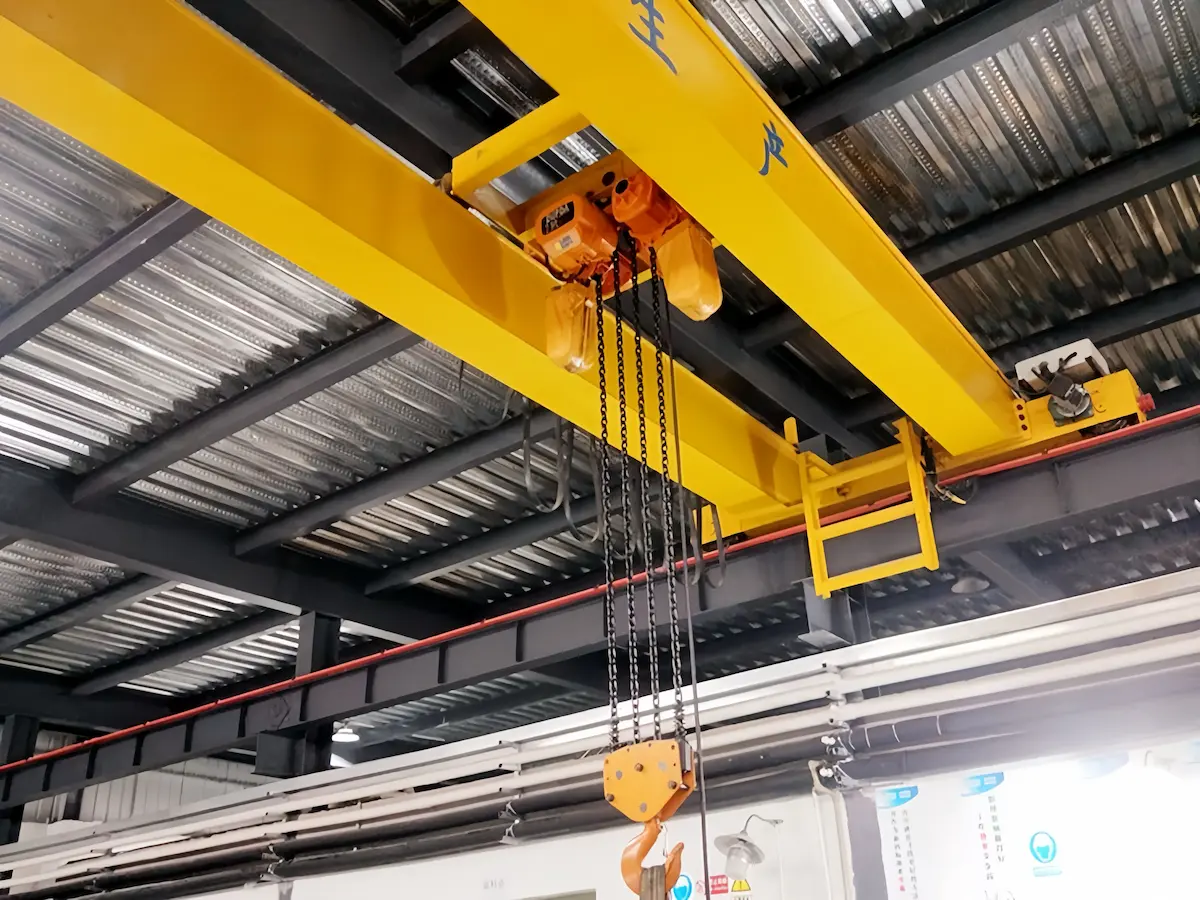
As the core lifting mechanism in lifting equipment, the electric hoist is widely used in overhead cranes, jib cranes, and various light-duty lifting devices, undertaking critical tasks such as material handling, equipment installation, and production line operations. Its performance and reliability directly affect the operating efficiency and safety of the entire lifting system. In practical applications, improper selection of an electric hoist may result in unstable operation, reduced productivity, or even safety risks. It can also increase maintenance requirements and operating costs over time, negatively impacting normal production activities. Therefore, selecting the right electric hoist based on specific working conditions is particularly important.
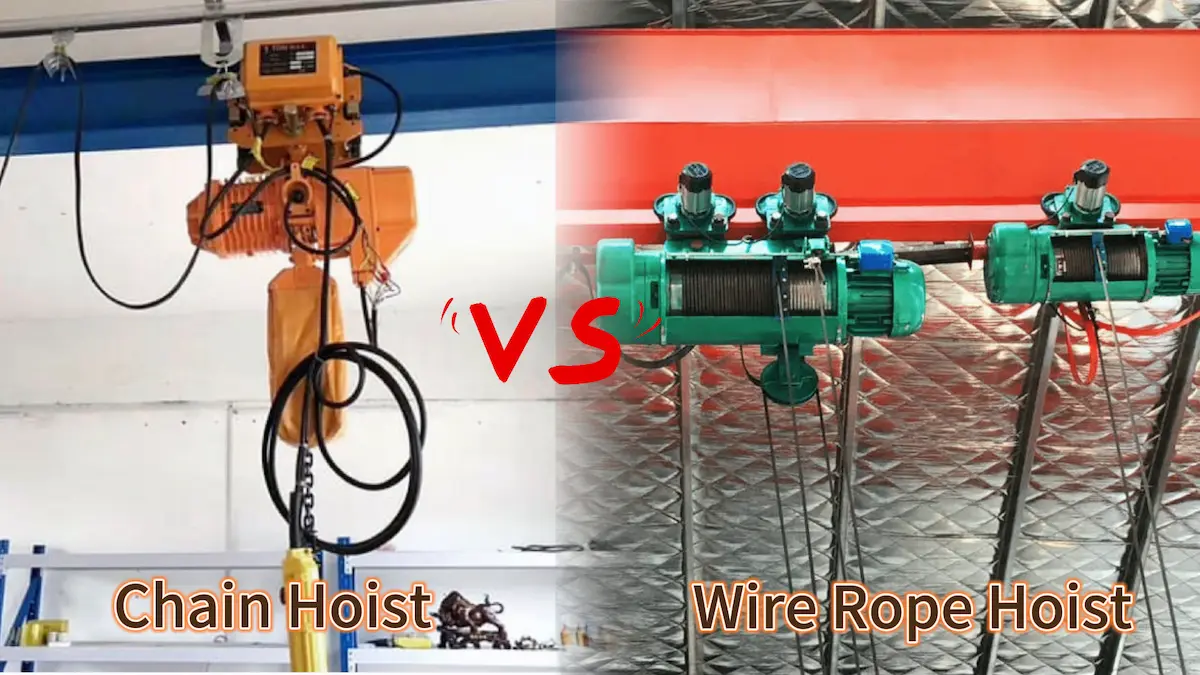
At present, the chain hoist and the wire rope hoist are the two most widely used types of electric hoists in industrial applications. Each has its own advantages in terms of structural characteristics, load capacity, and application scenarios. A clear understanding of their differences is essential for achieving safe and efficient lifting operations.
Chain Hoist Overview
Working Principle and Structural Features
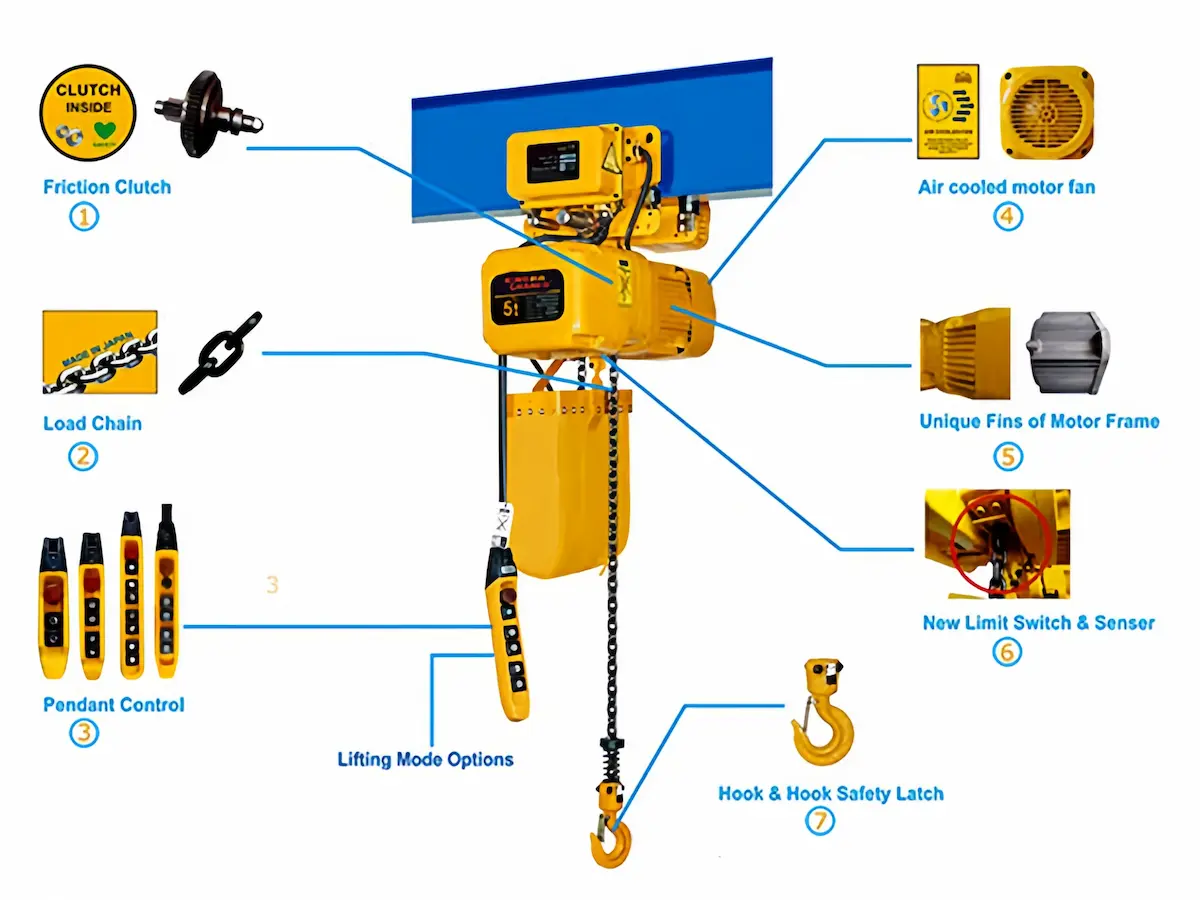
Working principle: A chain hoist uses a high-strength lifting chain as the load-bearing element. The motor drives a reduction mechanism, allowing the chain wheel to circulate the lifting chain to raise or lower the load.
Structural features: It mainly consists of a motor, gearbox, chain wheel, lifting chain, hook, and control system. The compact structure and small installation footprint make it particularly suitable for confined spaces or applications requiring precise handling.
Typical lifting capacity: Chain hoists are generally used for light to small-medium lifting operations, with common capacities ranging from 0.5 to 5 tons. Although special designs can achieve higher capacities, industrial applications are mainly focused on light and medium-duty conditions.
Key Advantages of Chain Hoists
▴Simple structure and low self-weight, making installation and maintenance convenient.
▴Smooth lifting motion and sensitive braking, enabling accurate positioning—ideal for assembly lines, equipment maintenance, and mold handling where precision is critical.
▴Relatively low maintenance workload and lower routine inspection costs.
Limitations of Chain Hoists
▴Due to limitations in chain length and transmission method, chain hoists have relatively restricted lifting height and speed, making them unsuitable for large lifting heights or high-frequency, high-speed operations.
▴For applications requiring long travel, heavy loads, or continuous high-efficiency operation, a wire rope hoist is generally a better choice.
Wire Rope Hoist Overview
Working Principle and Main Components
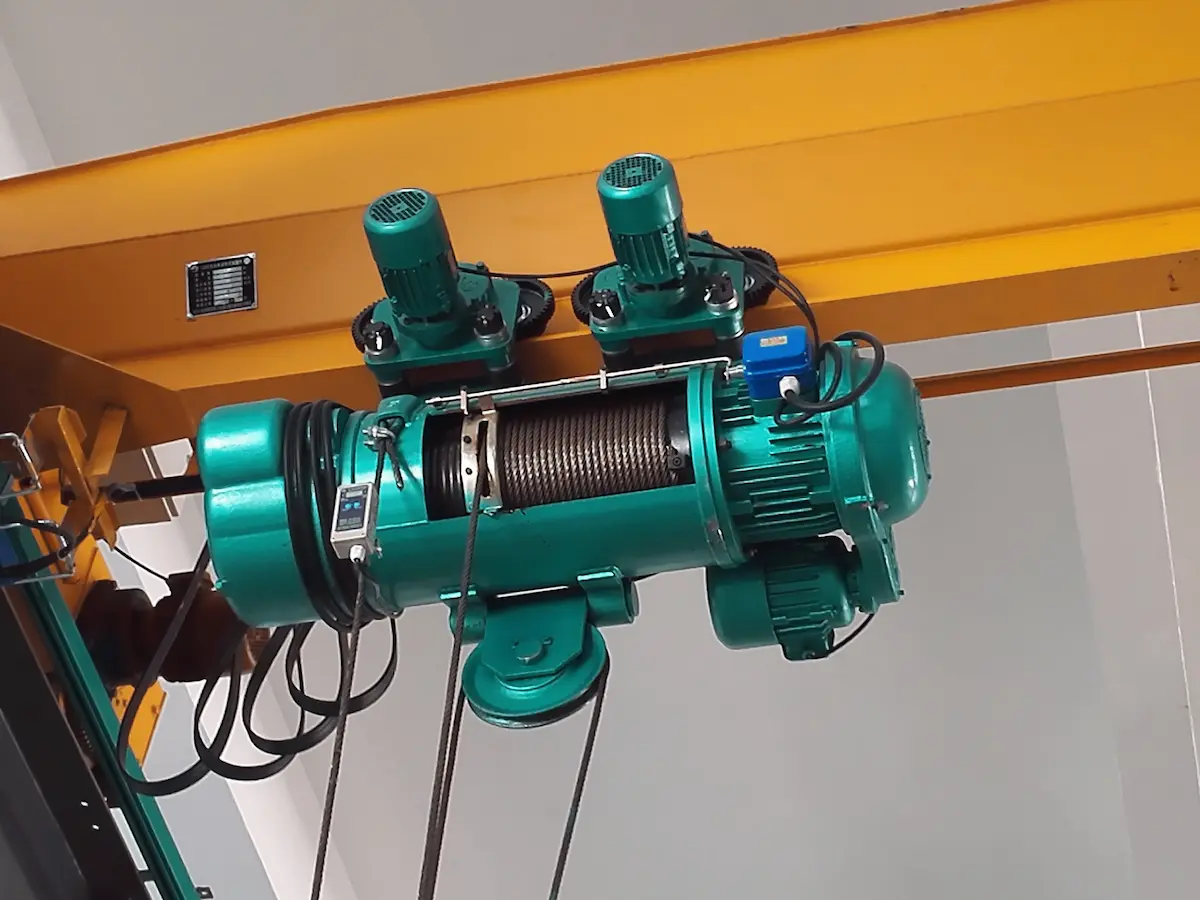
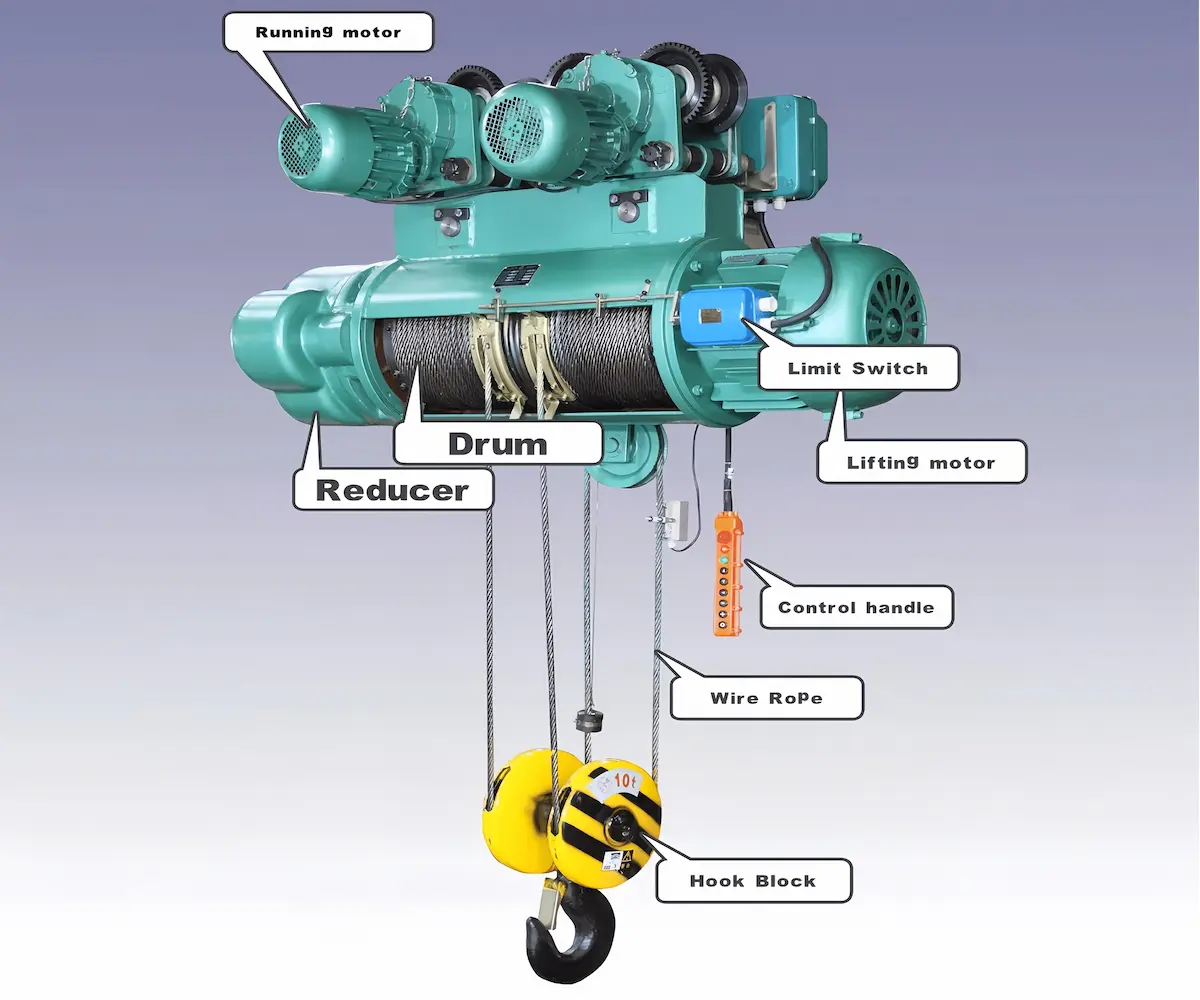
Working principle: A wire rope hoist uses steel wire rope as the load-bearing and traction element. The motor drives the drum to rotate, winding or unwinding the wire rope in an orderly manner to raise or lower the load.
Main components: Key components include the lifting motor, reducer, drum, wire rope, pulley block, hook, and electrical control system. This design offers high transmission efficiency and uniform load distribution, making it suitable for heavier loads and intensive operations.
Typical lifting capacity: Wire rope hoists are designed for medium to heavy-duty lifting, with common capacities ranging from 3 tons up to 100 tons or more. They can be customized according to actual working conditions and are widely used in over
Core Advantages of Wire Rope Hoists
▴Compared with chain hoists, wire rope hoists offer higher lifting capacities and faster lifting speeds, making them well suited for high-frequency and continuous-duty applications.
▴Smooth operation and high efficiency, ideal for industries such as steel manufacturing, machinery production, and warehousing and logistics where productivity and load capacity are critical.
Limitations of Wire Rope Hoists
▴The structure is relatively more complex, requiring higher standards for installation, commissioning, and maintenance.
▴Components such as wire ropes, pulleys, and drums require regular inspection and replacement, resulting in higher overall maintenance costs compared with chain hoists.
▴When selecting a wire rope hoist, factors such as operating frequency, maintenance conditions, and long-term operating costs must be carefully evaluated.
Core Comparison Between Chain Hoists and Wire Rope Hoists
In practical lifting applications, chain hoists and wire rope hoists each demonstrate advantages under different working conditions. There are clear differences between the two in terms of load capacity, structural design, operating efficiency, and maintenance requirements. Properly understanding these core distinctions helps improve operating efficiency and control overall costs while ensuring safety.
|
Comparison Item |
Chain Hoist |
Wire Rope Hoist |
| Lifting medium | Lifting chain | Wire rope |
| Working principle | Chain wheel drives the chain in a circulating motion | Drum drives the wire rope to wind/unwind |
| Typical lifting capacity | ≤ 5 t (mainly light-duty) | 3 t–100 t and above |
| Lifting height | Relatively limited by chain length | Greater lifting height, suitable for long lift travel |
| Lifting speed | Relatively slower | Faster lifting speed, multiple speed options |
| Duty class | Medium to low duty class | Suitable for high duty class and high-frequency operation |
| Structural features | Compact structure, low self-weight | More complex structure, larger overall size |
| Installation space requirement | Small; suitable for low headroom or space-limited sites | Requires larger installation space |
| Positioning accuracy | High; ideal for precision assembly | Good accuracy, slightly lower than chain hoists |
| Operating smoothness | Smooth; suitable for intermittent operation | Very smooth; suitable for continuous operation |
| Maintenance difficulty | Simple maintenance, fewer inspection items | Higher maintenance requirements; regular wire rope inspection needed |
| Typical applications | Assembly lines, equipment maintenance, mold handling | Steel mills, machinery manufacturing, heavy warehousing & logistics |
| Compatible cranes | Single-girder cranes, jib cranes | Single- or double-girder overhead cranes, gantry cranes |
Selection Recommendations for Different Application Scenarios
In real engineering and industrial projects, electric hoist selection should comprehensively consider factors such as working environment, lifting capacity, operating frequency, and safety requirements. Different scenarios emphasize different performance priorities. Proper selection not only improves efficiency but also reduces failure rates and total life-cycle costs.
|
Application Scenario |
Working Characteristics |
Recommended Hoist Type |
Selection Rationale |
Key Considerations |
| Production line assembly, equipment maintenance, light-duty tasks | Light loads, intermittent operation, high positioning accuracy required | Chain hoist | Compact structure and low self-weight enable precise operation and fine adjustment | Limited installation space; ensure chain length meets lifting height |
| Warehousing, mold handling, medium-duty tasks | Moderate loads, medium operating frequency, certain lifting speed required | Chain hoist or wire rope hoist | • Chain hoist: suitable for small–medium loads with high positioning accuracy
• Wire rope hoist: suitable for frequent lifting and larger lifting heights |
Select based on actual load and lifting height; pay attention to maintenance |
| Steel mills, equipment manufacturing, heavy industrial applications | Large loads, long lift travel, continuous high-frequency operation | Wire rope hoist | High lifting capacity and fast lifting speed; ideal for continuous heavy-duty operation | Use with large cranes; regularly inspect wire ropes and drums |
| Indoor environments | Limited space; requirements for low noise and operator comfort | Chain hoist or wire rope hoist | Flexible selection based on load and operating frequency | Check headroom and installation space; ensure safe operation |
| Outdoor or harsh environments | High temperature, humidity, dust, or corrosive conditions | Wire rope hoist (with high protection rating) | Robust structure and durability meet harsh environmental demands | Equip with protective covers, anti-corrosion treatment, high-IP motors; perform regular inspections |
Key Parameters and Considerations for Electric Hoist Selection
In practical engineering applications, selecting an electric hoist in a scientific and well-structured manner requires a comprehensive evaluation of multiple key parameters to ensure lifting operations are safe, reliable, and cost-effective.
Rated Capacity and Safety Factor
Definition
The rated capacity refers to the maximum load an electric hoist can safely lift, while the safety factor indicates the hoist’s ability to operate safely under rated load conditions.
Selection recommendations
When selecting a hoist, sufficient capacity margin should be reserved based on actual load requirements. In general, the rated capacity should be 1.25–1.5 times the actual working load, ensuring safe operation under occasional overloads or dynamic loads.
Notes
Never select a hoist with a rated capacity close to or lower than the actual working load, as this may lead to safety incidents and equipment damage.
Lifting Height and Duty Class
Lifting height
Determines the required chain length or drum size, directly affecting travel design and overall equipment dimensions.
Duty class
Defined by FEM and ISO standards, the duty class specifies allowable operating frequency and duration.
Selection recommendations
▴Short lifting height and intermittent operation → lower duty class hoist
▴Long lifting height and continuous, high-frequency operation → higher duty class hoist
Notes
Ensure the chain length or drum capacity fully meets the maximum lifting height to avoid over-travel or unsafe operation.
Voltage, Control Method, and Protection Rating
Voltage
Select according to the crane system and site power supply. Common industrial voltages include 380V, 400V, 415V, 440V, and 690V.
Control method
Options include push-button control, pendant control, wireless remote control, or variable frequency drive (VFD) control. The choice affects operational flexibility and safety.
Protection rating
The IP rating defines dust and water resistance, determining suitability for different environments.
Selection recommendations
▴Indoor environments: standard protection rating
▴Outdoor or harsh environments: higher IP rating and corrosion-resistant materials
Notes
Ensure the control system is compatible with the crane type and operating habits, while fully complying with applicable safety standards.
Compatibility with Overhead Cranes or Single-Girder Cranes
Requirements
The electric hoist must match the crane type, span, lifting height, and load capacity.
Selection recommendations
▴Single-girder cranes: suitable for light to medium-duty chain hoists or small-capacity wire rope hoists
▴Double-girder cranes: suitable for medium to heavy-duty wire rope hoists, meeting high-capacity and high-frequency requirements
Notes
Improper matching may result in unstable crane operation, abnormal structural loading, and even serious safety risks.
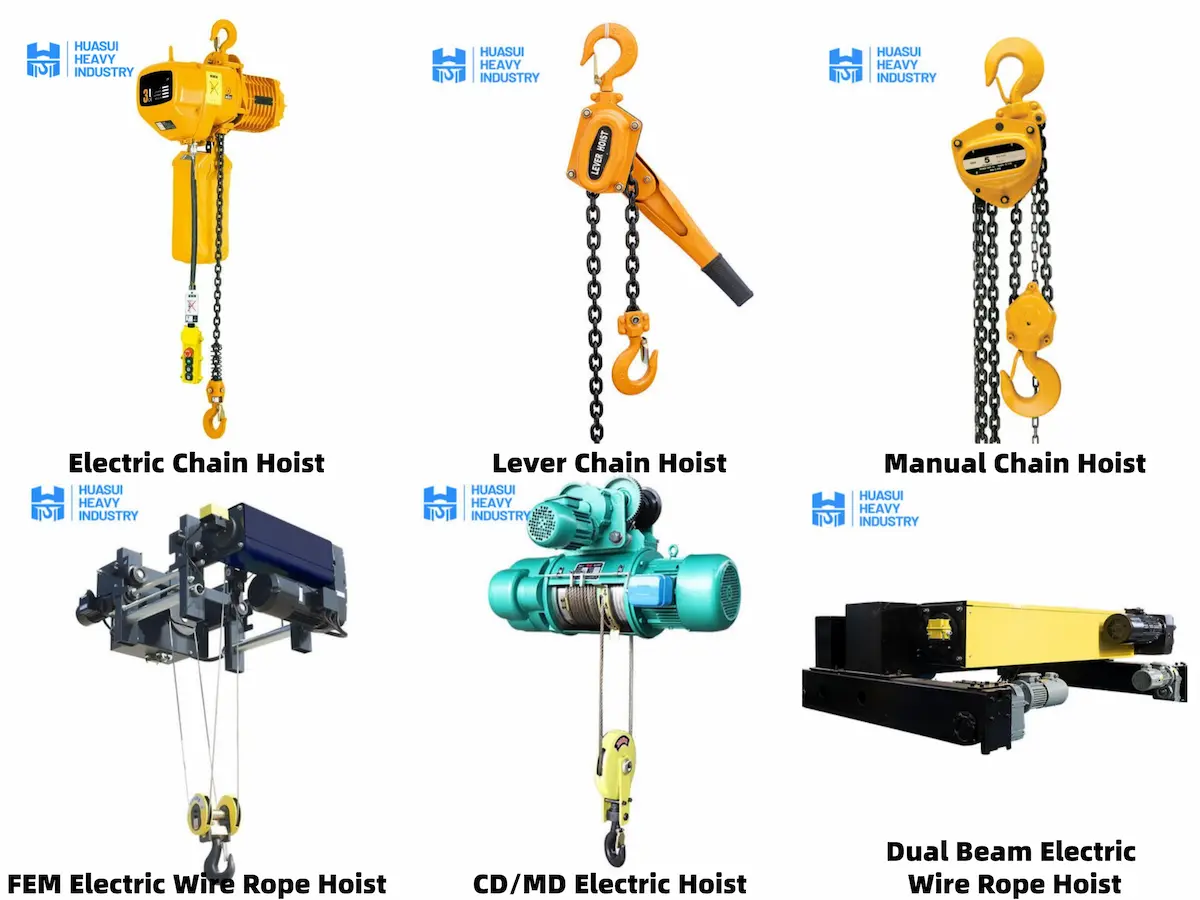
Core Advantages of HSCRANE Electric Hoists
▴Comprehensive product range: HSCRANE offers a full lineup of chain hoists and wire rope hoists, covering light-duty to heavy-duty applications across various industrial scenarios.
▴Strong customization capability: Hoists can be customized in terms of rated capacity, lifting height, voltage, control method, and protection rating to precisely match actual working conditions.
▴High safety standards: Key components are manufactured from high-strength materials and equipped with multiple safety features such as overload protection and limit switches, ensuring safe and reliable lifting operations.
▴Stable and reliable performance: Designed for high-frequency and continuous operation, HSCRANE hoists run smoothly with long service life, reducing failure rates and maintenance frequency.
▴International certifications: Products comply with FEM, ISO, CE, and other international standards, making them suitable for export and overseas projects with assured global reliability.
▴Comprehensive service support: HSCRANE provides professional selection guidance, technical support, and after-sales service to help customers reduce operational risks and maximize equipment efficiency.
The application boundaries between chain hoists and wire rope hoists are clear. Chain hoists are ideal for light-duty, intermittent operations requiring high positioning accuracy, while wire rope hoists are better suited for medium to heavy loads, high-frequency, and continuous operations. Selecting the right electric hoist must always follow the principle that working conditions determine selection. Only by comprehensively evaluating actual load, lifting height, operating frequency, and environment can safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness be ensured.
For complex or special working conditions, professional technical support is essential. HSCRANE offers complete selection guidance, customized solutions, and reliable after-sales service to help customers reduce risk, improve efficiency, and achieve long-term stable operation.
Contact HSCRANE today to obtain an electric hoist solution tailored to your specific application and make your lifting operations safer and more efficient.
Looking for solutions for heavy loads and long lifting travel? Click to explore Winch: The Power Player in Modern Engineering and discover professional lifting solutions tailored to your project needs.