Abstract:
This article systematically explains the critical role of crane anti-collision system solutions in enhancing equipment reliability and operational safety. It points out that as cranes evolve toward larger capacities, higher speeds, and multi-crane coordinated operations, the risks of collision, overload, and structural damage increase significantly, making anti-collision systems a core component of modern crane safety architectures. Starting from definitions and functions, the article details the working principles of anti-collision systems, their main components (such as overload protection, height and travel limiters, buffers, and wind protection devices), as well as the integration methods and applicable operating conditions of different system types. It further analyzes the comprehensive value of anti-collision systems in reducing accidents, lowering maintenance costs, extending service life, and complying with international standards, and highlights HSCRANE’s technical strengths in system integration, high-reliability design, intelligent control, and customized solutions—providing clear and practical guidance for selecting appropriate crane anti-collision solutions.
In modern industrial production, port logistics, and shipyard manufacturing, cranes are increasingly developing toward larger capacities, higher operating speeds, and multi-crane coordinated operations. The simultaneous operation of multiple cranes within the same working area significantly tightens the available operating space between cranes and between cranes and building structures. Under complex working conditions and high-frequency operations, operational risks rise markedly.
Due to operator error, limited visibility, delayed equipment response, or control system failures, crane collision accidents still occur from time to time. Typical scenarios include collisions between cranes, trolley or travel mechanisms impacting end beams, hook over-hoisting, and chain failures caused by structural overload. Such incidents not only damage critical components and reduce equipment reliability, but may also result in unplanned downtime and serious safety hazards.
Against this backdrop, the crane anti-collision system, as a vital component of modern crane safety systems, plays an irreplaceable role in preventing collision accidents and ensuring long-term stable operation by continuously monitoring operating conditions, providing early warnings, and implementing automatic limiting and protective control.
Definition and Function of Crane Anti-Collision Systems
Concept and System Positioning
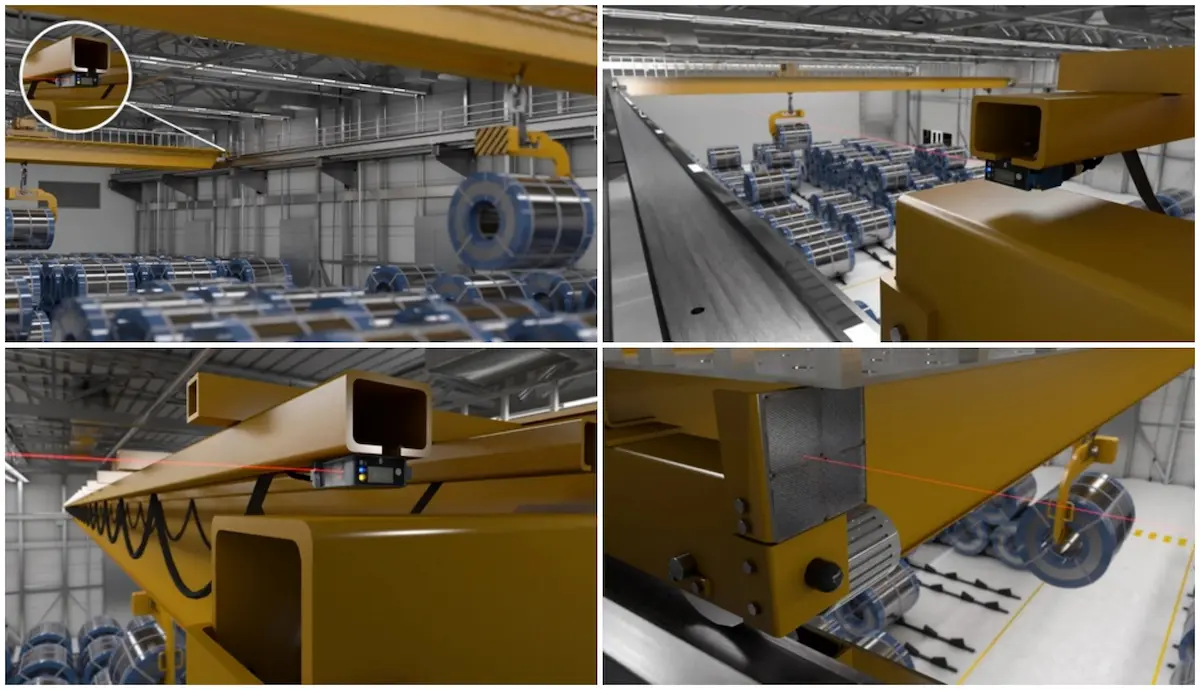
▪Crane anti-collision system: A comprehensive safety protection system installed on cranes and their operating mechanisms to monitor crane motion status, load conditions, and hazardous zones in real time. When a crane approaches predefined safety limits or faces risks of collision or overload, the system intervenes through warnings, speed reduction, motion limiting, or automatic shutdown to effectively prevent accidents.
▪System positioning: An anti-collision system is not a single component, but a highly integrated part of the crane’s electrical control system, limit devices, and safety protection architecture, serving as a key element of modern crane safety systems.
Comprehensive Safety Role in Preventing Collisions, Overloads, and Structural Damage
In practical operation, crane anti-collision systems provide multi-layer protection against various risks:
▪By means of distance detection, position control, and buffer protection, they prevent collisions between cranes, between cranes and building structures, or at end-limit positions.
▪In combination with overload protection and height/travel limiting functions, they effectively avoid structural damage and critical component failures caused by overload or misoperation.
This multi-level safety mechanism helps reduce impact loads and abnormal wear, minimizing the adverse effects of accidents on the crane structure and drive systems.
Significance for Improving Equipment Reliability and Operational Safety
From a long-term operational perspective, anti-collision systems are not only essential for ensuring operational safety but also a key configuration for improving crane reliability and stability. By reducing collision incidents and sudden failures, these systems significantly lower maintenance costs and unplanned downtime, extend equipment service life, and provide strong support for safe, efficient, and continuous production.
Overall Working Principle of Crane Anti-Collision Systems
▪Signal acquisition and evaluation: The system collects real-time data on crane position, load, and travel through sensors and detection devices. The control unit then performs logical analysis to identify potential collision or limit-exceeding risks.
▪Integrated system control: The anti-collision system is closely integrated with the crane’s electrical control system. Once protective conditions are triggered, it can issue commands such as speed reduction, motion limiting, or operation prohibition to the drive system, enabling automatic safety intervention.
▪Multi-level protection strategy: Through staged protection—early warning, speed reduction, limiting, and emergency stop—the system intervenes progressively before the crane reaches hazardous zones, preventing collisions while minimizing impact on structural components.
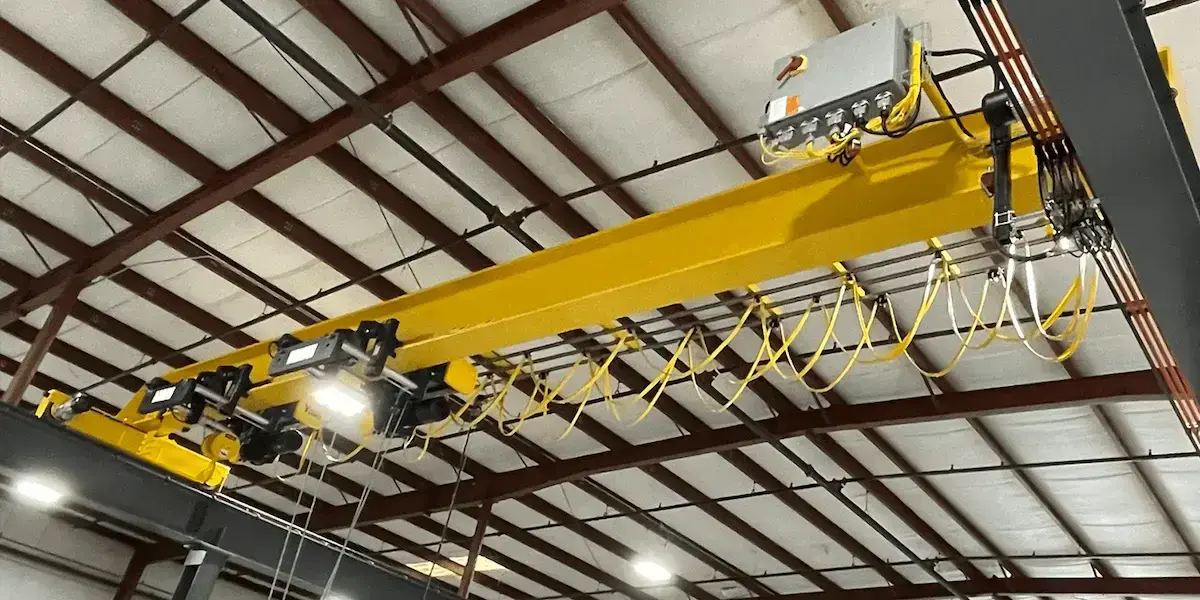
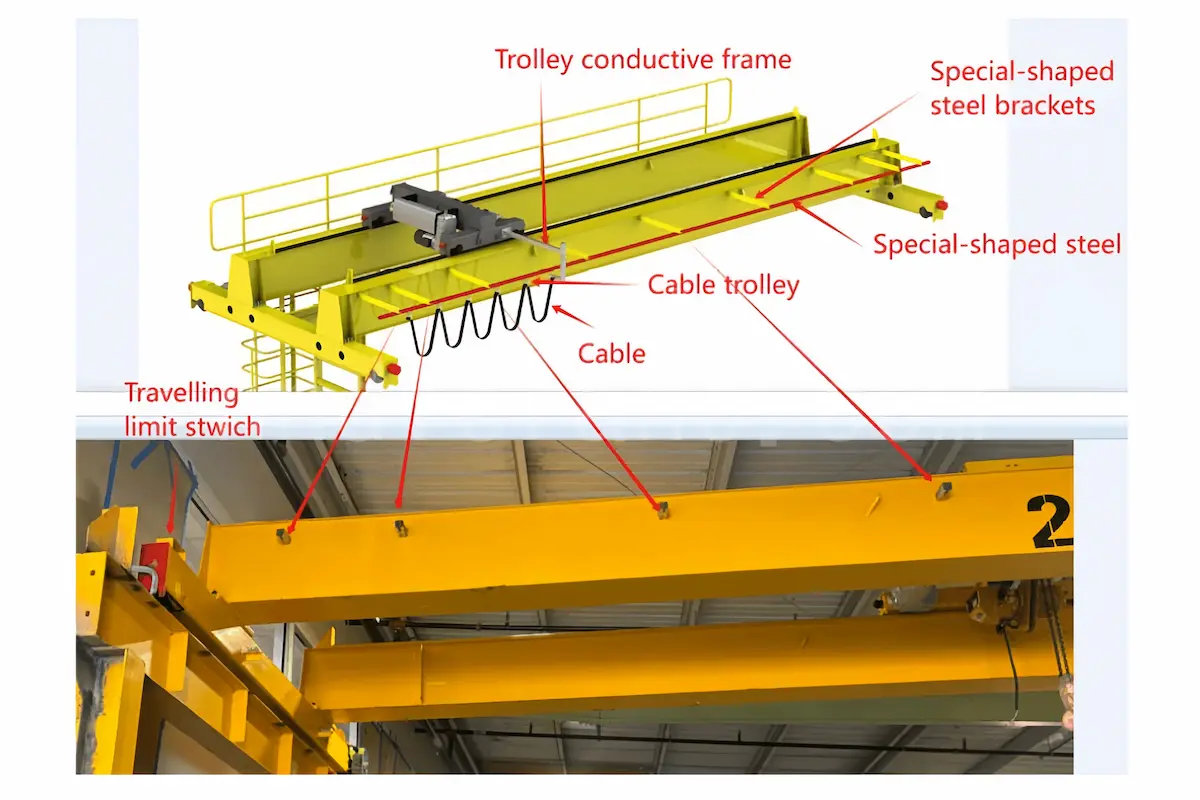
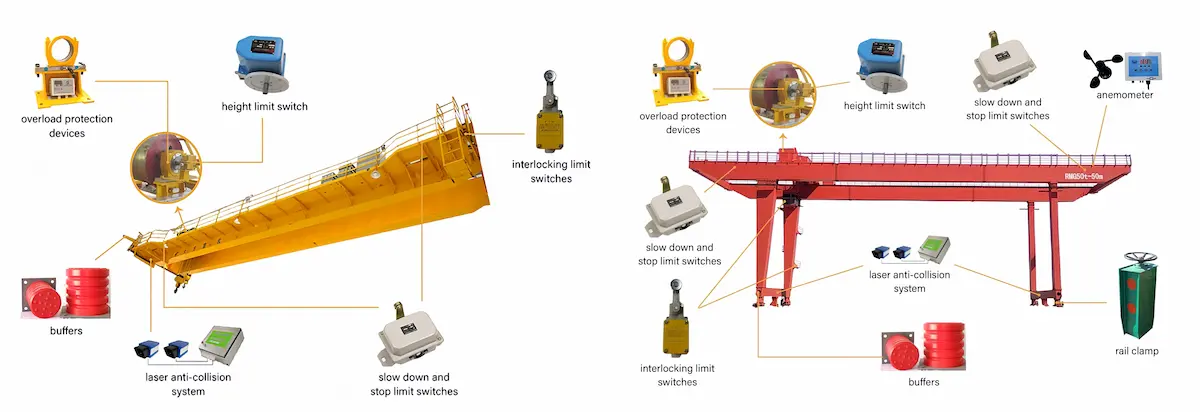
Main Components of a Crane Anti-Collision System
A crane anti-collision system is composed of multiple safety protection units working in coordination. Each component controls crane operating risks from different aspects—such as load, lifting height, travel range, impact energy, and environmental factors. Through systematic configuration and interlinked control, these systems effectively reduce the probability of collision accidents and enhance overall crane reliability and safety levels.
Overload Protection Device
The overload protection device continuously monitors the actual lifting load of the crane. When the load approaches or exceeds the rated capacity, the system automatically issues an alarm and can restrict or cut off lifting motions to prevent overload operation. This device effectively avoids structural deformation, mechanism damage, and secondary collision risks caused by overload, forming a fundamental safeguard for long-term stable crane operation.
Crane Height Limit Switch
The height limit switch restricts the maximum lifting height of the hook or hoisting mechanism. When the hook approaches the preset height, the system intervenes in advance to prevent dangerous situations such as hook over-hoisting or wire rope overwinding. This device protects the hoisting mechanism, motor, and key transmission components, reducing equipment damage caused by extreme operating conditions.
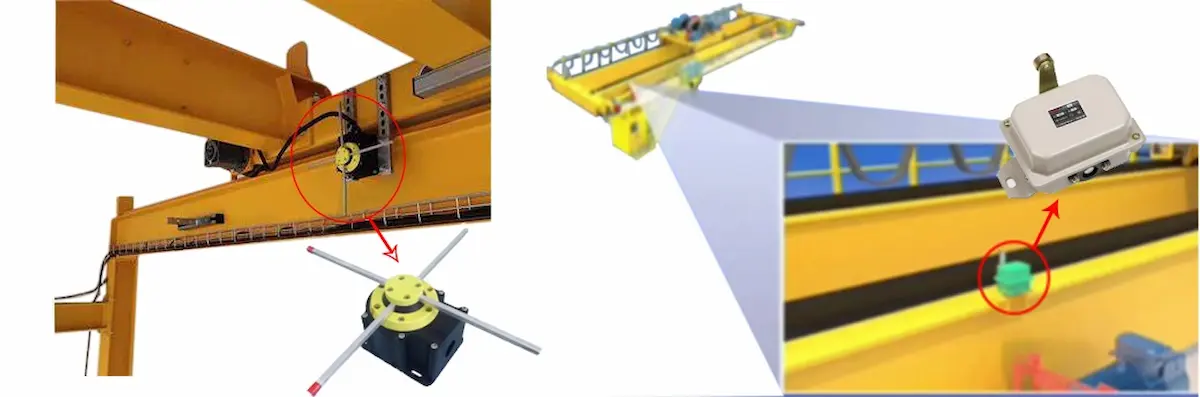
Deceleration and Stop Limit Switches
Deceleration and stop limit switches are usually installed in pairs. As the crane or trolley approaches the end of its travel, the deceleration switch is triggered first to ensure smooth operation. When the extreme position is reached, the system forcibly stops motion in the corresponding direction. This graded limiting method not only improves operational smoothness but also provides essential safety redundancy for the crane anti-collision system.
Crane Buffers
Buffers are installed at the end of the crane or trolley travel path to absorb impact energy generated at limit positions or during accidental contact. By reducing collision impact forces, buffers effectively protect steel structures, travel mechanisms, and crane rails, reduce structural fatigue, and extend the overall service life of the equipment.
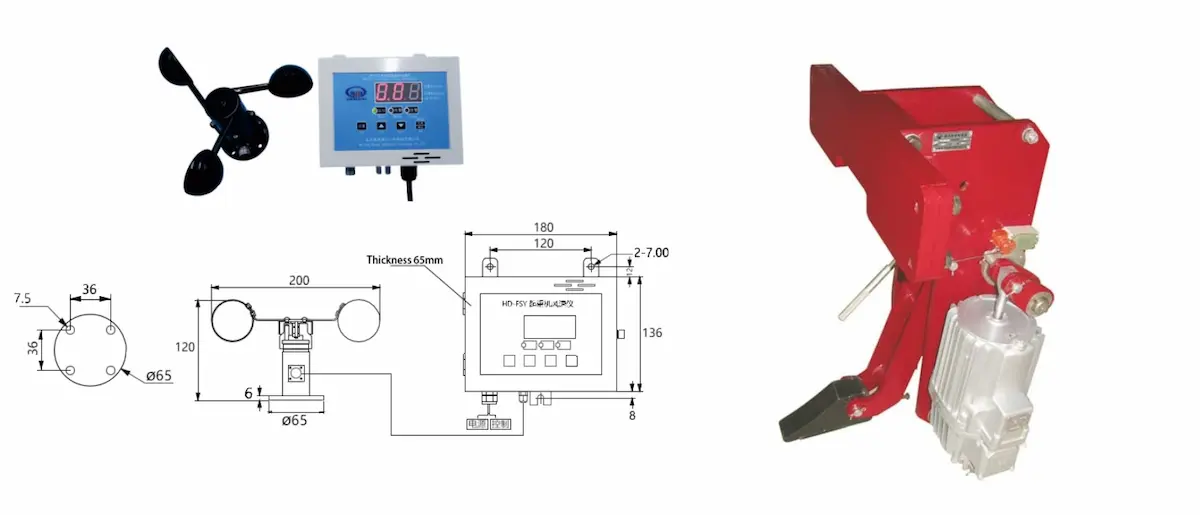
Wind Protection Devices
Wind protection devices are mainly applied to outdoor or port cranes to prevent sliding, loss of control, or overturning under strong wind conditions. By mechanically or electrically securing the crane in place, these devices improve stability in harsh weather environments and are critical safety configurations for preventing structural collisions and major accidents.
System Integration and Types of Crane Anti-Collision Systems
Crane anti-collision systems can be configured in various forms depending on control methods, system integration levels, and operating conditions. Through rational system integration, anti-collision devices can work synergistically with limit switches, overload protection, and electrical control systems, meeting the safety requirements of different cranes and working environments.
|
Anti-Collision System Type |
Integration Method |
Main Functional Features |
Applicable Conditions |
| Mechanical anti-collision device | Independent mechanical structure, no direct linkage with electrical systems | Simple structure, direct response, physical contact limits motion | Single crane, low-frequency operation, basic protection needs |
| Electrical limit anti-collision system | Linked with crane electrical control circuits | Uses limit switches to achieve deceleration, stopping, and directional restriction | Conventional industrial workshops, standard overhead crane or gantry crane |
| Electrical + mechanical combined anti-collision | Coordination of mechanical buffering and electrical control | Combines active control and passive energy absorption, higher safety redundancy | Cranes with long travel distances and higher operating speeds |
| Multi-crane anti-collision system | Integrated with PLC or safety control systems | Real-time monitoring of multiple crane positions to prevent mutual collisions | Workshops with multiple overhead cranes operating simultaneously |
| Intelligent anti-collision system | Deep integration with electrical control and safety systems | Supports multi-level warning, deceleration, limiting, and emergency stop | High-frequency operation, complex conditions, highly automated applications |
Key Characteristics of Anti-Collision System Integration
▪High level of systemization: Anti-collision devices can be integrated with overload protection, height limits, and travel limits into a unified safety control system for centralized management.
▪High intervention priority: When hazardous conditions are detected, the anti-collision system can take priority control and forcibly intervene in crane operation.
▪Flexible configuration: Modular combinations can be implemented based on crane type, operating speed, working environment, and required safety level.
Through appropriate selection and integration of crane anti-collision system types, cranes can meet safety regulations while achieving higher operational reliability and improved working efficiency.
The Key Value of Crane Anti-Collision Systems in Enhancing Equipment Reliability
With the continuous improvement of crane system integration, the crane anti-collision system has evolved from a single safety accessory into a critical system that directly affects equipment reliability and operational efficiency. Its core value is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
▪Effectively reducing collision accidents and equipment damage: Through graded control mechanisms such as early warning, deceleration, limiting, and emergency stop, anti-collision systems can proactively intervene before hazardous conditions occur. This significantly reduces the risk of collisions between cranes or between cranes and surrounding structures, minimizing damage to key components and steel structures at the source.
▪Lowering maintenance costs and the risk of unplanned downtime: Collision accidents are often accompanied by structural deformation, mechanism damage, and prolonged downtime. By implementing early intervention and energy absorption, anti-collision systems effectively reduce the frequency of sudden failures, lower maintenance intensity and spare parts consumption, shorten unplanned downtime, and improve equipment availability.
▪Improving overall operational stability and service life: By applying deceleration and staged limiting control when approaching hazardous areas, anti-collision systems avoid frequent emergency stops and high-impact operation. This helps reduce long-term fatigue effects on transmission systems, electrical components, and steel structures, thereby enhancing overall crane stability and extending service life.
▪Enhancing safety levels and meeting international standards: Well-designed anti-collision systems support compliance with international safety standards such as CE and ISO, providing reliable assurance for equipment export, project acceptance, and long-term operation.
Advantages of HSCRANE Crane Anti-Collision Solutions
Based on a deep understanding of crane safety and equipment reliability, HSCRANE treats the crane anti-collision system as an integral part of the overall safety architecture. Through systematic design and engineering implementation, HSCRANE delivers highly reliable anti-collision solutions for a wide range of operating conditions.
▪Strong system integration capability: HSCRANE anti-collision systems can be highly integrated with overload protection, height limits, travel limits, wind protection devices, and other safety systems, while maintaining stable interaction with the crane electrical control system. Unified control logic and priority management ensure coordinated operation of all safety devices, significantly enhancing safety redundancy and operational reliability.
▪High-reliability design: HSCRANE adopts proven components and rational redundancy configurations in anti-collision system design. Safety systems are designed to meet Performance Level d (PL d) requirements, ensuring high reliability and safety integrity even under critical fault conditions. The systems are capable of long-term stable operation under high-frequency, heavy-load, and complex working conditions, with carefully selected key components to minimize false triggering and failure risks caused by environmental changes or load fluctuations.
▪Intelligent control logic: HSCRANE anti-collision solutions support multi-level protection strategies, including warning, deceleration, limiting, and emergency stop. The system automatically applies appropriate control actions based on risk level, ensuring safety while minimizing negative impacts on equipment structure and operational efficiency, thus achieving an optimal balance between safety and reliability.
▪Customized solutions: For different crane types, travel configurations, and operating environments, HSCRANE provides customized anti-collision solutions, including single-crane protection, multi-level anti-collision systems, and comprehensive safety configurations for complex conditions. This ensures a high degree of alignment between the anti-collision system and actual applications.
▪International standards compliance: HSCRANE crane anti-collision systems are designed in accordance with international crane safety standards such as CE and ISO. This provides reliable support for equipment export, project acceptance, and long-term operation, helping customers reduce compliance risks and enhance overall project value.
Recommendations for Selecting a Crane Anti-Collision Solution
When selecting a crane anti-collision solution, it is essential to comprehensively evaluate the operating environment, required safety level, and equipment characteristics to ensure stable and reliable performance under real working conditions.
|
Selection Focus |
Key Considerations |
Recommended Guidance |
| Operating environment | Indoor/outdoor use, wind loads, spatial complexity | For outdoor or port applications, configure wind protection devices and multi-level anti-collision protection |
| Crane type | Overhead crane, gantry crane, port crane, etc. | Match anti-collision and limit configurations to crane structure and travel characteristics |
| Operating frequency & load | High-frequency operation, heavy or variable loads | Use high-reliability components and redundant designs for demanding conditions |
| Anti-collision system type | Mechanical, electrical, or intelligent systems | Intelligent systems are recommended for multi-crane operation or complex conditions |
| System integration capability | Compatibility with electrical control, limits, overload protection | Prioritize highly integrated solutions to improve overall reliability |
| Maintenance & expandability | Ease of inspection, future upgrade potential | Modular designs reduce maintenance costs and expansion risks |
| Standards & compliance | CE, ISO, and other regulatory requirements | Ensure compliance with project and export market regulations |
| Supplier capability | Engineering experience, technical support, service | Choose manufacturers with proven project experience and strong support capabilities (such as HSCRANE) |
The crane anti-collision system is a core safeguard for long-term safe operation and operational reliability. Through the integrated application of overload protection, height and travel limits, buffers, wind protection devices, and intelligent control logic, anti-collision systems not only prevent collision accidents effectively, but also reduce maintenance costs, extend equipment service life, and ensure safe, efficient operation in multi-crane and complex working environments.
HSCRANE is committed to providing customized, comprehensive, and highly integrated anti-collision solutions for all types of cranes. Whether in industrial workshops, port terminals, or heavy-duty lifting environments involving high-value equipment, we deliver reliable configurations that meet international standards and ensure both equipment and operational safety.
Contact HSCRANE today to obtain a professional anti-collision solution and comprehensively upgrade the safety and reliability of your cranes.
FAQ
Q1: What is a crane anti-collision system and what is its function?
A1: A crane anti-collision system is a key part of the crane safety system. Through overload protection, height and travel limits, buffers, wind protection devices, and intelligent control logic, it prevents collisions, overloads, and structural damage, improving operational safety and reliability.
Q2: Which types of cranes are anti-collision systems suitable for?
A2: HSCRANE anti-collision systems are applicable to overhead cranes, gantry cranes, port cranes, and industrial cranes operating in multi-crane environments. Configurations can be customized based on travel range, load, and operating conditions.
Q3: Do HSCRANE anti-collision systems comply with international safety standards?
A3: Yes. HSCRANE anti-collision systems are designed in compliance with international crane safety standards such as CE and ISO, ensuring regulatory compliance and supporting export project acceptance.
Q4: How does an anti-collision system improve crane reliability?
A4: By continuously monitoring position, load, and operating status, the system applies graded responses—warning, deceleration, limiting, and emergency stop—to reduce collision incidents, minimize equipment damage, lower maintenance costs, and extend service life.
Q5: How should I choose the right anti-collision solution?
A5: Selection should be based on operating environment, crane type, operating frequency, load characteristics, and required safety level. High integration, ease of maintenance, compliance with international standards, and strong supplier engineering support are key factors.
Q6: Can an anti-collision system be retrofitted to existing cranes?
A6: Yes. Existing cranes can be retrofitted with anti-collision systems after technical evaluation, without major structural modification. The systems can be integrated with existing overload and limit devices, significantly improving safety and reliability. HSCRANE supports retrofit and upgrade services for crane anti-collision systems.
To learn more about how crane buffers absorb impact and enhance service life and anti-collision safety, click here:
What Is a Crane Buffer? A Complete Guide to Types and Functions
This document is for reference only. Specific operations must strictly comply with local laws and regulations and equipment manuals.